2. 前记
多愁善感,就是我也是我旁边的很多人,总是想太多,尤其是我,做的却很少,想的过程中消耗了太多精力,以至于只有想了
但「火山」明显不一样,他是个恰恰相反的人
在成长的道路上,一个很重要的事情就是看清自己
「到底是什么」 这个专题,目前可以分为俩种类型:
- 以极少的术语解释一件之前已经进行过探究的事情
- 以极少的术语见识一件事情,再引出极大的点来研究
这篇文章就是第二种
3. spring中bean是线程安全的吗?
不是
spring中bean有单例(默认)、多例模式(prototype)
在单例中,如果这个bean是有状态的,就会有多线程的竞争
举个例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
package constxiong.interview.threadsafe;
/**
* 计数类
* @author ConstXiong
* @date 2019-07-16 14:35:40
*/
public class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public void addAndPrint() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(++count);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="counter" class="constxiong.interview.threadsafe.Counter" />
</beans>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
package constxiong.interview.threadsafe;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class CounterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring_safe.xml");
for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) {
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
Counter counter = (Count;er)context.getBean("counter");
for (int j = 0; j <1000; j++) {
counter.addAndPrint();
}
}
}.start();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 不是我们想要的结果,打印出 10000。
1
5
7
4
2
6
3
8
9
.
.
.
9818
9819
9820
9821
9822
9823
9824
9825
3. 如何解决
-
通过
ThreadLocal去解决线程安全(每个线程单独计数) -
通过
AtomicInteger解决(线程直接累加计数)
3.1 ThreadLocal是什么
This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its get or set method) has its own, independently initialized copy of the variable. ThreadLocal instances are typically private static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g., a user ID or Transaction ID).
看看官方文档是怎么解释的:
这个类提供 thread-local(线程-本地)变量。这些变量不同于普通的变量,在每个线程中访问他自己的变量(通过他的get或者set方法),在每个线程中独立的初始化这个变量。ThreadLocal 实例通常作为一个私有的属性在一个类中,用来关联一个线程中的状态(比如一个用户ID或者是事务ID)
自我感觉翻译的还是挺准确的,差不多是直译的,也有进行一些变换,这也是最近学精读的一个强技巧:只看一遍,不回头
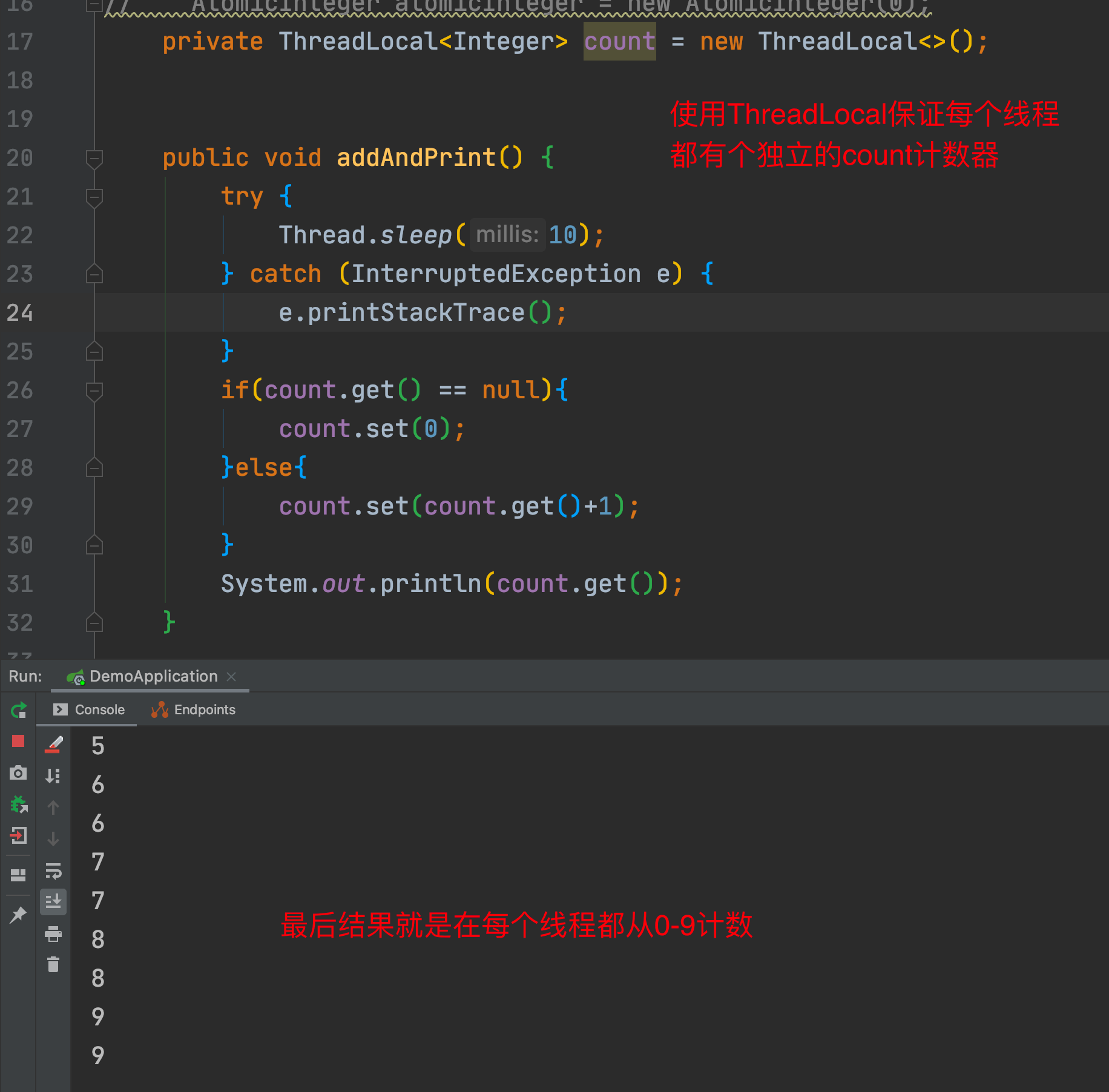
3.2 AtomicInteger 解决
还有一种解决是通过 AtomicInteger解决的
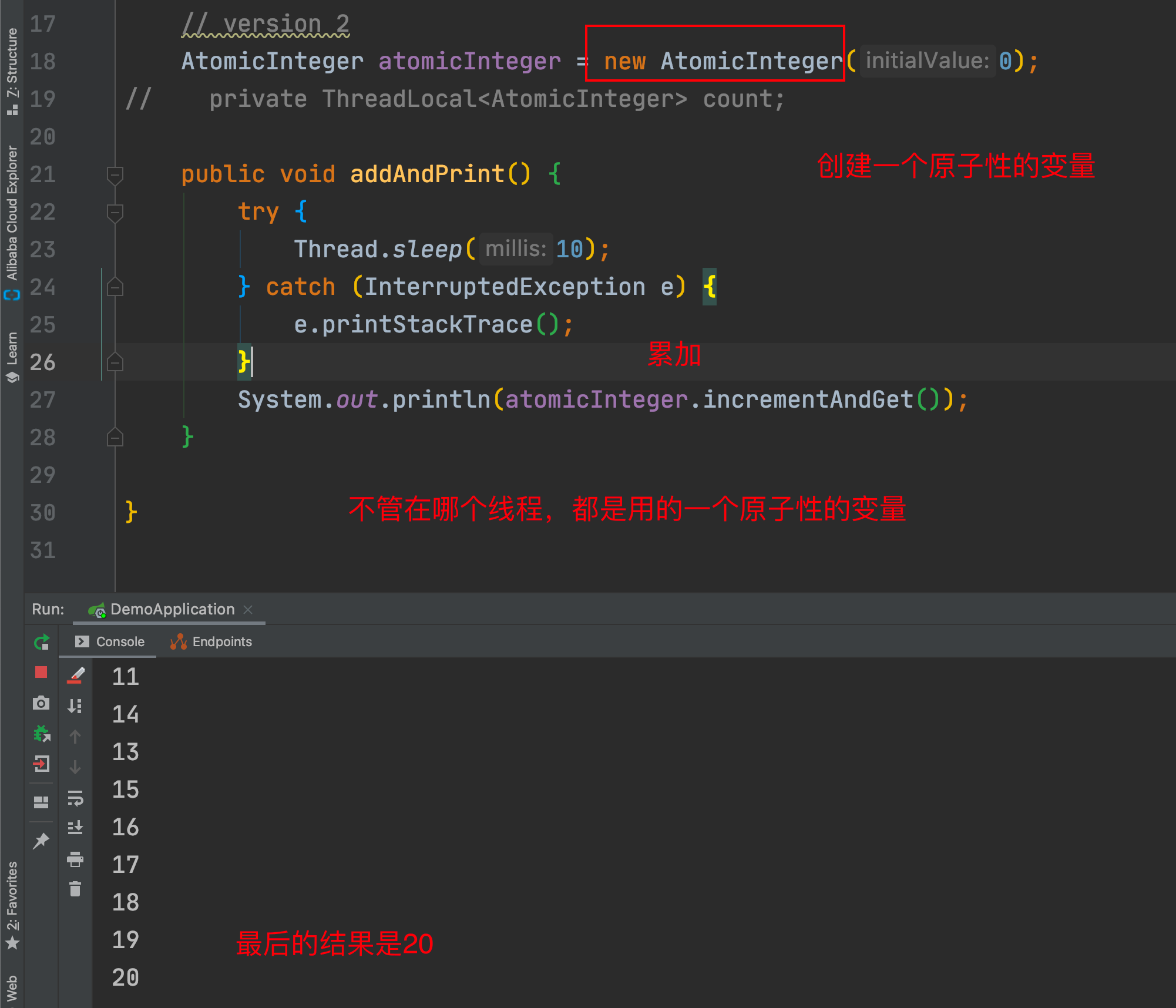
4. 总结
这篇文章通过 bean 的线程安全问题,引出了 ThreadLocal 和 AtomicInteger
ThreadLocal 是一个只能在该线程中获取的变量
那么ThreadLocal 到底怎么实现的呢,下篇文章见
reference
https://www.javanav.com/interview/f612753aef3e477dbaaf6648fa69fa38.html
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/ThreadLocal.html